Dental X-Rays 101
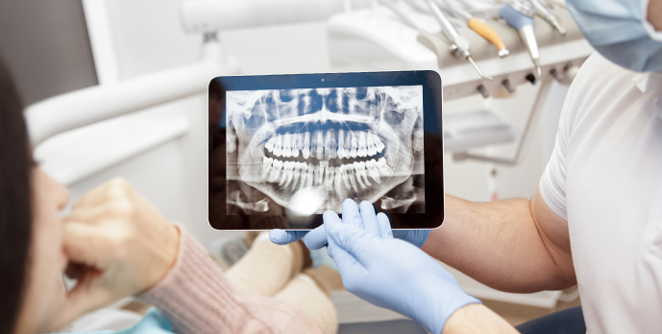
Want to get a clear picture of your oral health? Dental X-rays are a valuable option! They’re a common diagnostic tool used by dentists to capture an accurate image of the mouth – including teeth and gums.
Dental X-rays, also referred to as radiographs, use low doses of radiation to help your dentist identify oral health issues early on, which can help avoid more complex health issues and costly treatments in the future.
Types of X-rays
There are two main types of dental X-rays:
- Intraoral X-rays place X-ray film inside the mouth and are the most common type of X-ray. That’s because they allow dentists to find cavities, check the health of teeth roots, bone surrounding teeth and the status of developing teeth.
- Extraoral X-rays are taken with the X-ray film outside of the mouth. This type focuses on the larger view of your jaw and skull.
Common dental X-rays:
- Bitewing: Looks for cavities in back teeth. It requires patients to gently bite down on small dental film packets or a reusable digital image receptor.
- Periapical: Focuses on teeth roots and the bone surrounding the teeth by capturing images of two to three teeth at a time.
- Panoramic: This machine rotates around the patient’s head to capture an image of all the teeth and jaw bones.
- Cone Beam CT: Uses 3D imaging that allows dentist to see the teeth, jaws and surrounding anatomy.
Who are dental X-rays for?
The short answer: everyone! Dental X-rays help dentists detect a variety of dental and overall health issues in both adults and children.
For adults, dental X-rays are taken to:
- Diagnose tooth decay
- Visualize an abscess on a tooth
- Determine if there is any bone loss, often associated with gum disease
- Diagnose the need for braces, dentures, or other dental procedures
- Look for any abnormalities, including cysts and tumors
For children, dental X-rays are taken to:
- Diagnose tooth decay
- Monitor erupting teeth in younger children
- Check wisdom teeth development
- Look for any abnormalities, including cysts and tumors
Dental X-ray safety
X-rays recommendations are commonly based on individual oral health needs and the patient’s risk for dental disease. They can help dentists determine the best treatment options and avoid unnecessary procedures.
When dental X-rays are necessary, dentists and their staff are equipped to minimize radiation exposure. Fortunately, modern technology and digital imaging only subject patients to a minimal amount of radiation exposure compared to the natural radiation exposure we experience from the sun every day, so you can take comfort in your safety.
Don’t hesitate to ask questions concerning your safety prior to a dental X-ray. Your dentist should be able to provide information on how they reduce radiation exposure for patients. It’s also important to note that dental X-rays are generally safe during pregnancy. With low amounts of radiation and the body’s exposure mainly limited to the head, risk is minimal. However, it’s recommended that patients speak with their doctor and dentist beforehand to ensure both the patient and child remain protected.
Like routine cleanings, dental X-rays are key to practicing preventive care and protecting your oral and overall health. For more information, talk to your dentist at your next appointment.


Add comment